- An information system that provides reports to stakeholders about the economic activities and condition of a business.
- Financial accounting: The area of accounting that focuses on recording transactions and events so that general-purpose financial statements can be prepared.
- Managerial accounting: The branch of accounting that aids management in making financing, investing, and operating decisions for the company.
- The head of the accounting department in a company is called comptroller or chief financial officer (CFO).
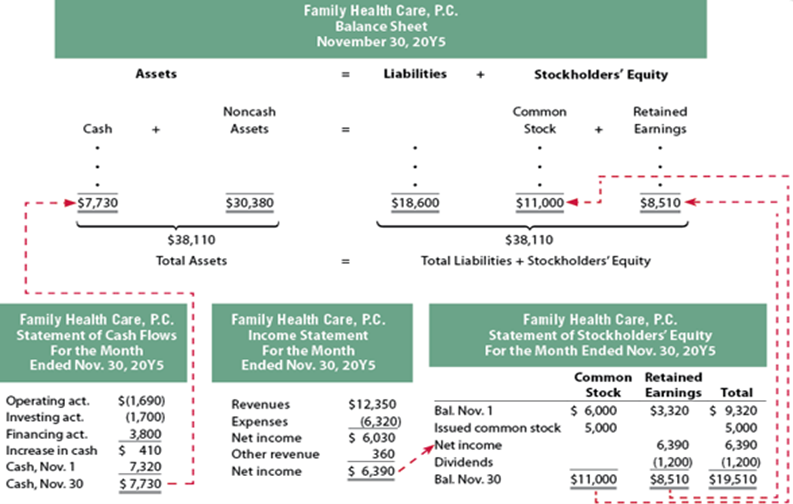
Statement of stockholders’ equity: A financial statement that reports the change in financial condition due to the changes in stockholders’ equity items for a specific period of time.
Retained earnings: Net income retained in a corporation. (Beginning retained earnings + Net income – Dividends = Ending retained earnings)
Stockholders’ equity: The stockholders’ rights to the assets of a business.
Assets = Liabilities + stockholder’s Equity
Statement of cash flows: Provides a summary of the cash receipts and cash payments and reports the change in financial condition due to the change in cash during a specific period of time.
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB): The authoritative body that has the primary responsibility for developing accounting principles.
Financial accounting system: A system that includes:
- (1) a set of rules for determining what, when, and the amount that should be recorded for an economic event;
- (2) a framework for facilitating preparing financial statements; and
- (3) one or more controls to determine whether errors could have occurred in the recording process.
Cash basis of accounting: A system of accounting in which only transactions involving increases or decreases of the entity’s cash are recorded. (Practiced in Chapter 2)
- Under the cash basis of accounting, net income and net cash flows from operating activities are equal.
Accrual Basis of Accounting: A system of accounting in which revenue is recorded as it is earned, and expenses are recorded and matched against the revenue they generate.
- Under the accrual basis of accounting, net income and net cash flows from operating activities may be significantly different.
- Revenue is recorded when it is earned, expense when expense is incurred in generated revenue, and adjusting entries required in order to prepare financial statements.





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed


